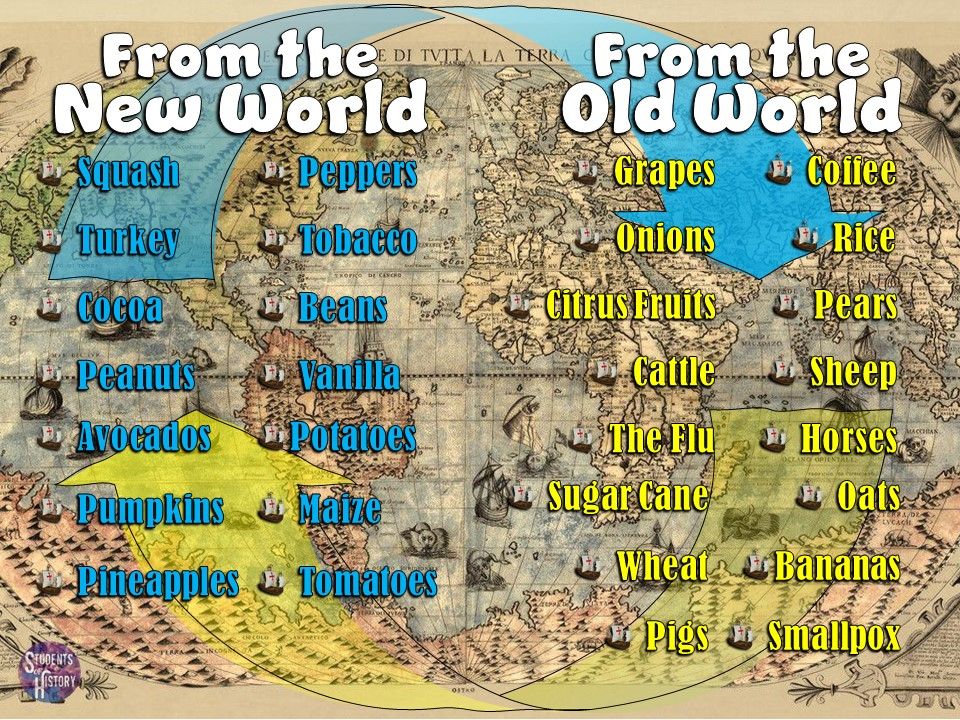
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of plants, animals, diseases, and culture between the Americas and the Old World during the 15th and 16th centuries. During this exchange, both the Americas and the Old World experienced significant impacts in terms of their biodiversity, economies, and population dynamics.
This phenomenon had far-reaching consequences and shaped the course of world history. We will delve into the details of the Columbian Exchange, exploring its causes, effects, and significance in shaping the modern world as we know it today. We will examine the various elements that were exchanged, the consequences of this exchange, and the long-term impacts it had on different regions of the world.
By understanding the Columbian Exchange, we can gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of global history and the transformative power of transcontinental trade.

Credit: www.britannica.com
The Origins Of The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of biological, cultural, and technological elements between the Old World and the New World that took place following Christopher Columbus’s arrival in the Americas in 1492. This exchange had a profound impact on both sides of the Atlantic and played a crucial role in shaping the modern world.
Exploration and discovery of the New World opened up new opportunities for trade and exchange. European explorers like Columbus, Amerigo Vespucci, and Hernando Cortes played key roles in this exchange, introducing new crops, animals, and diseases to the Americas while also bringing back precious metals, such as gold and silver, to Europe. This exchange of resources drastically altered the economic, social, and ecological landscapes in both hemispheres.
The significance of the Columbian Exchange cannot be overstated. It revolutionized global trade, led to the rise of European colonialism, and contributed to the development of modern agriculture, medicine, and culture. By understanding its origins and key players, we can better grasp the far-reaching consequences of this transformative historical event.
The Impact Of New World Commodities On The Old World
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread exchange of goods, ideas, culture, and diseases between the Old World (Europe, Africa, and Asia) and the New World (the Americas) during the Age of Exploration. This exchange had a profound impact on both worlds and dramatically changed their respective landscapes.
Introduction to the exchange of goods between the Old and New Worlds:
One of the key aspects of the Columbian Exchange was the introduction of new crops and plants to the Old World. Important plants such as maize, potatoes, tomatoes, and tobacco were brought from the New World to Europe, Asia, and Africa. These new crops not only expanded the food supply but also played a crucial role in shaping the diets and agricultural practices of the Old World. In return, the Old World introduced crops such as wheat, barley, and rice to the New World.
Analysis of the economic effects on the Old World:
The economic effects of the Columbian Exchange on the Old World were significant. The introduction of new crops from the Americas resulted in increased agricultural productivity, leading to population growth and urbanization. The availability of new resources also fueled the growth of industries such as sugar production, textile manufacturing, and mining. Moreover, the exchange of goods led to the emergence of powerful trading empires and the establishment of global trade routes.
In summary, the Columbian Exchange had a profound impact on both the Old and New Worlds, shaping their economies, cultures, and environments. The exchange of goods, particularly the introduction of new crops and plants, played a crucial role in transforming societies and setting the stage for further exploration and globalization.
The Transfer Of Animals And Diseases In The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of animals and diseases between the Old World (Europe, Asia, and Africa) and the New World (the Americas) during the 15th and 16th centuries. This exchange had significant impacts on both regions, shaping the course of history and transforming societies.
One aspect of the Columbian Exchange was the introduction of Old World animals to the New World. Europeans brought domesticated animals such as horses, cattle, pigs, and sheep, which had a profound impact on the Native American cultures. These animals provided new sources of food, labor, and transportation, but they also posed challenges for indigenous populations as they competed with native wildlife and disrupted ecosystems.
The transfer of diseases was another crucial aspect of the Columbian Exchange. Native Americans had no immunity to the diseases from the Old World, which were brought over by European explorers and settlers. This resulted in devastating epidemics, decimating the indigenous populations and changing the course of history in the Americas.
On the other hand, the impact of New World diseases on the Old World population was not as dramatic. While the diseases from the New World did spread to Europe, Africa, and Asia, the population in these regions had already developed some immunity to certain types of diseases. However, the exchange of diseases did have a notable impact on the Old World, contributing to shifts in population demographics and patterns of disease transmission.
In conclusion, the Columbian Exchange had far-reaching effects on both the Old World and the New World. It transformed economies, societies, and ecosystems, and its impact can still be seen in today’s world.
Cultural Exchange And Transformation In The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange was a period of cultural exchange and transformation that occurred following the European exploration and colonization of the Americas. This exchange resulted in the transfer of various aspects of culture including language, art, and music between the Old World and the New World.
Languages played a significant role in the Columbian Exchange as European languages such as Spanish, English, and Portuguese were brought to the Americas while Native American languages influenced the development of pidgin languages. This linguistic exchange led to the creation of new dialects and languages.
In terms of art, European styles and techniques greatly influenced Native American art, resulting in a fusion of artistic traditions. Native American weaving techniques, pottery, and other crafts were also adopted and adapted by European settlers.
Similarly, music was another cultural aspect that underwent transformation during the Columbian Exchange. Indigenous musical styles and instruments were introduced to Europe, while European musical traditions influenced the development of new musical genres in the Americas.
The Columbian Exchange not only facilitated the exchange of cultural aspects but also led to the transformation and adaptation of cultures. The interaction between different cultures resulted in the synthesis of traditions and the creation of new cultural practices, traditions, and identities.
The Columbian Exchange And Global Trade
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, and technology between the Americas and the Old World during the 15th and 16th centuries. This exchange had a profound impact on global trade and shaped the course of history. The introduction of new crops, such as maize, potatoes, and tomatoes, boosted agricultural productivity and led to population growth in Europe. European diseases, on the other hand, decimated indigenous populations in the Americas. Along with the exchange of goods and diseases, the Columbian Exchange reshaped trading routes and practices. It connected the previously isolated regions and introduced new trading networks, contributing to the rise of capitalism. Furthermore, this exchange had long-term effects on global economies. The influx of precious metals from the Americas fueled European economies and expanded global trade. The Columbian Exchange represents a turning point in history, creating a new era of globalization.
Legacy And Contemporary Significance Of The Columbian Exchange
Legacy and Contemporary Significance of the Columbian Exchange The Columbian Exchange, a profound event in history, has left a lasting impact on various aspects of our world. This transformative period of transatlantic exchange between the Old World and the New World introduced a myriad of flora, fauna, and diseases that reshaped societies, economies, and ecosystems. The consequences of this exchange are still evident in modern society, with cultural fusion, globalization, and multiculturalism being direct outcomes. In terms of agriculture, the Columbian Exchange sparked a revolution in food production and consumption, transforming diets, introducing new crops, and altering farming practices around the globe. Moreover, the environmental impact of this exchange cannot be overlooked. The introduction of non-native species and modification of habitats caused ecosystem disruptions and changes. However, it is crucial to note that the Columbian Exchange is not without controversy. Ongoing debates surround its labeling as an equal exchange or as a form of imperialism, as well as its role in the spread of disease and the displacement of indigenous populations. Examining the lasting significance of the Columbian Exchange allows us to better understand the complexities and implications of this historical event.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is A Columbian Exchange
What Was The Columbian Exchange And Why Is It Important?
The Columbian Exchange refers to the exchange of goods, people, and ideas between the Americas and Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. It had a significant impact on both continents, with the introduction of crops, animals, and diseases transforming societies and ecosystems.
This exchange shaped modern globalization and had long-lasting consequences.
What Were The Positive Effects Of The Columbian Exchange?
The Columbian Exchange brought positive effects such as the introduction of new crops such as potatoes and tomatoes in Europe, which improved diets and led to population growth. It also facilitated the exchange of knowledge and ideas, sparking advancements in science, technology, and agriculture.
Additionally, it fostered cultural interactions, leading to the enrichment of diverse traditions and practices.
What Were The Negative Consequences Of The Columbian Exchange?
Despite its benefits, the Columbian Exchange also had negative consequences. The transfer of diseases from Europe to the Americas, such as smallpox and measles, resulted in catastrophic population declines among indigenous people. The introduction of non-native animals and plants led to environmental imbalances and the displacement of native species.
Additionally, the exchange fueled the transatlantic slave trade, causing immense human suffering and exploitation.
Conclusion
The Columbian Exchange was a transformative event that shaped the world we know today. It brought together different cultures and introduced new plants, animals, and diseases to both the Old World and the New World. This exchange had far-reaching consequences, changing economies, diets, and demographics around the globe.
We can still see its impact in our society and environment, making it a topic of historical and cultural significance. Understanding the Columbian Exchange helps us appreciate the interconnectedness of our world and the complexities of our shared history.